اصطلاحات فیزیوتراپی

فیزیوتراپی یا توانبخشی از روش های درمانی عارضه های ارتوپدی و اسکلتی بدن بوده که با به کارگیری تکنیک ها و متدهای مختلف دستی و غیردستی و تمیرنات ورزشی موجب بهبود وضعیت آسیب و عوارض اسکلتی استخوانی نواحی مختلف بدن (پا، دست، سر، گردن، کمر و...) می شوند. پزشکان و متخصصین فیزیوتراپی مانند دیگر متخصصین از اصطلاحات و لغات خاصی استفاده می کنند که هر کدام یا به یک عارضه، مشکل و آسیب اشاره دارد و یا مربوط به تکنیک های درمانی می باشند. اصطلاحات فیزیوتراپی مخصوص فیزیوتراپیست ها و متخصصین ارتوپدی می باشد و ممکن است پزشکان با تخصص های دیگر نیز این اصطلاحات را نشناسند. افراد عادی نیز معمولا چیزی از این اصطلاحات نمی دانند و حتی گاهی پیش می آید که درمورد روش درمان و یا خود عارضه ایجاد شده اطلاعی نداشته و از لغات اشتباهی برای تعریف عارضه و درمان خود استفاده کنند. اگر شما نیز مایل هستید بیشتر در مورد این اصطلاحات و علم فیزیوتراپی بدانید و مانند متخصصین ارتوپدی و فیزیوتراپی بتوانید از اصطلاحات صحیح، مناسب، علمی و تخصصی استفاده کنید، همراه ما باشید. در این بخش شما را با اصطلاحات رایج و کاربردی فیزیوتراپی آشنا خواهیم کرد.
Bursitis is the inflammation of a bursa, a small fluid filled sac that sits between muscles, tendons and bones to reduce friction.
Congenital muscular torticollis (CMT) or wry neck is a condition in infants detected at birth or shortly after. It is characterized by rotational deformity of the cervical spine with secondary tilting of the head. There is a lateral head tilt to one side and contralateral rotation. It is most commonly the result of unilateral shortening and thickening or excessive contraction of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The basic abnormality is known as endomysial fibrosis with deposition of collagen and migration of fibroblasts around individual muscle fibers. It leads to a limitation of the head mobility in both rotation and lateral flexion and progressive degrees of neck contracture.
The Active Cycle of Breathing Techniques (ACBT) is an active breathing technique performed by the patient and can be used to mobilise and clear excess pulmonary secretions and to generally improve lung function.
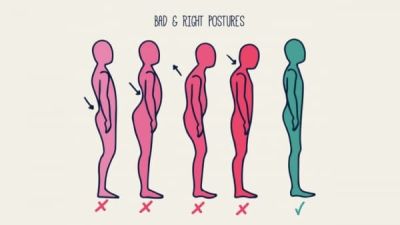
Posture is the attitude assumed by body either when the body is stationary or when it is moving. Posture is attained as a result of coordinated action of various muscles working to maintain stability. Posture in easy terms can be understood as the position in which you hold your body when standing or sitting.
A fascia is a layer of fibrous tissue. A fascia is a structure of connective tissue that surrounds muscles, groups of muscles, blood vessels, and nerves, binding some structures together, while permitting others to slide smoothly over each other. Various kinds of fascia may be distinguished.
Like ligaments, aponeuroses, and tendons, fasciae are dense regular connective tissues, containing closely packed bundles of collagen fibres oriented in a wavy pattern parallel to the direction of pull. Fasciae are consequently flexible structures able to resist great unidirectional tension forces until the wavy pattern of fibres has been straightened out by the pulling force. These collagen fibres are produced by the fibroblasts located within the fascia.
Fasciae are similar to ligaments and tendons as they are all made of collagen except that ligaments join one bone to another bone, tendons join muscle to bone and fasciae surround muscles or other structures.
Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome (MTSS) or Shin-Splint Syndrome is a clinical pain condition defined as exercise-induced pain along the posteromedial tibial border (distal third) caused by repetitive loading stress during running and jumping[2]and provoked on palpation over a length of ≥5consecutive centimeters.
Manipulation is a passive technique where the therapist applies a specifically directed manual impulse, or thrust, to a joint, at or near the end of the passive (or physiological) range of motion. This is often accompanied by an audible ‘crack’. The common feature of spinal manipulation techniques is the fact that they achieve a pop or cracking sound within synovial joints. The cause of this audible release is open to some speculation but it is widely accepted to represent cavitation of a spinal facet joint. When there is a lower pressure than normal in the facet joint, gas bubbles are being formed in the joint. At the moment that the pressure rises, the bubble implodes, this is called cavitation.
It is a intervention Physiotherpists have been employing since the beginning of physical therapy practice. However, physiotherapists providing spinal manipulations have come under the scrutiny of other professions even though manipulation is not exclusive to any one domain or profession. The challenge has been brought forth to many state legislators because some chiropractors have argued that manipulations are not within the scope of physiotherapy practice. The APTA has created a page that delineates the difference between physical therapy manipulation and chiropractic manipulation. They have also published a manipulation education manual.
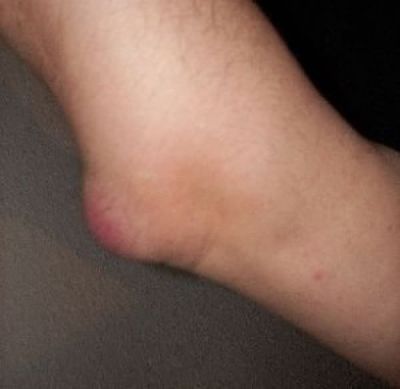
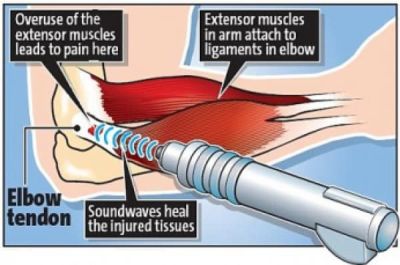
Lateral epicondylitis, also known as "Tennis Elbow", is the most common overuse syndrome in the elbow. It is a tendinopathy injury involving the extensor muscles of the forearm. These muscles originate on the lateral epicondylar region of the distal humerus. In a lot of cases, the insertion of the extensor carpi radialis brevis is involved.
Guillain Barre Syndrome(ghee-yan-bar syndrome) also known as landry's palsy is a classic lower motor neuron disorder. It is a reactive self limited auto-immune disease in which the body's immune system attacks part of the peripheral nervous system and which presents as acute generalized weakness.
It is referred to as a syndrome because it represents a broad group of demyelinating inflammatory poly radiculo-neuropathies.
Dystonia is defined as an involuntary contraction of the agonistic and antagonistic muscles, which can lead to repetitive involuntary movements and/or abnormal positions. this occurs most commonly in the hand, and is known as Focal Hand Dystonia.
The affected population includes individuals who require repetitive movements in their regular daily life, with one of the most affected populations being musicians and professional writers. In the European and American populations, Focal Dystonia varies its prevalence between 3 and 29.5 per 100.000 inhabitants.With dystonia occurring in musicians, it is estimated that 0.5 -1% of all musicans suffer some form of focal dystonia. These figures are highly variable if we individualize each case, depending on the instrument and the effort required with each performance; for example, the difference between a rhythm and a soloist guitar player.
This is the major inspiratory muscle (dome shaped) constructed of approximately 50% type 2 muscle fibres enabling fast,strong,prolonged low-tension contractions.
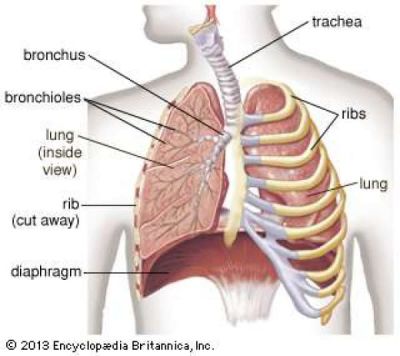
Asthma is a chronic lung disease and a very common respiratory condition. It is also known as a reactive airway disease which is inconvenient most of the time but manageable. Asthma attacks all age groups but often starts in childhood. It is a disease characterized by recurrent attacks of breathlessness and wheezing, which vary in severity and frequency from person to person. In an individual, they may occur from hour to hour and day to day.This condition is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they become easily irritated. In an attack, the lining of the passages swell causing the airways to narrow and reducing the flow of air in and out of the lungs.
A surgical operation to produce bony fusion across a joint,still occasionally preferred to joint replacement (arthroplasty) commonly done to correct such deformities as hammer toes or following certain complex fractures.
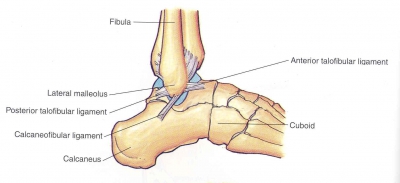
The weakest and most commonly injured ligament in the ankle is the anterior talofibular ligament. This is a lateral ligament, which means it consists of a band of connective tissue and is located on the outside of the ankle. It is near the posterior talofibular ligament.
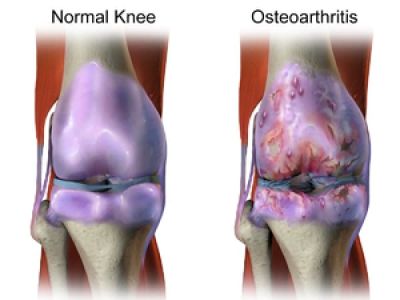
According to JAMA more than 10 million Americans are affected with knee osteoarthritis.Most commonly affecting a population age 45 and greater this condition occurs as the cartilage in the knee wears away eventually causing bone on bone contact between joint surfaces. Most common complaints include joint swelling, joint stiffness, and pain. Knee osteoarthritis can be diagnosis via radiographs indicating boney cysts, narrowing joint space, and scelrosing of the bone.
A 2017 review into reasons for the increased prevalence of knee OA reported that the recent increase in knee OA levels cannot simply be considered an inevitable consequence of people living longer. Iinstead is the result of modifiable risk factors, including but not limited to high BMI, that have become more common since the mid-20th century. From an evolutionary perspective, knee OA thus fits the criteria of a “mismatch disease” that is more prevalent or severe because our bodies are inadequately or imperfectly adapted to modern environments.
Knee osteoarthritis is the occurrence of osteoarthritis(OA) in the knee joint. Osteoarthritis has many definitions, but Kuttner et al . defined it as follows: “Osteoarthritis, also known as degenerative arthritis or degenerative joint disease, is a group of overlapping distinct diseases, which may have different etiologies but with similar biologic, morphologic, and clinical outcomes.”
Osteoarthritis involves the degradation of joints, including: articular cartilage; subchondral bone; ligaments; the capsule and the synovial membrane. This eventually leads to pain and loss of function.
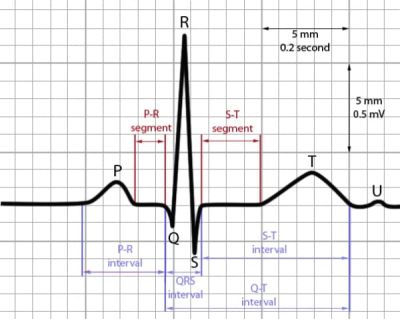
An electrocardiogram also termed an ECG or EKG (K means kardia for heart in Greek) or a 12 lead ECG. is a simple test that records the heart's electrical activity. The ECG machine is designed to recognise and record any electrical activity within the heart. It provides information about the function of the intracardiac conducting tissue of the heart and reflects the presence of cardiac disease through its electrical properties. Understanding ECG helps to understand how the heart works. With each heartbeat, an electrical impulse starts from the superior part of the heart to the bottom. The impulse prompts the heart to contract and pump blood.
Some heart problems are easier to diagnose when your heart is working hard and beating fast. During stress testing i.e. exercise ECG, exercise is used to make the heart work hard and beat fast while an EKG is done. If exercise can't be done, you'll be given medicine to make your heart work hard and beat faster. Heart rate and blood pressure will also be monitored throughout the test period. It usually takes about 7 to 12 minutes to complete.
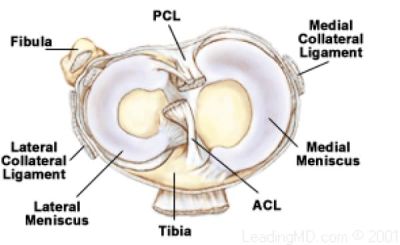
The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is a key structure in the knee joint, as it resists anterior tibial translation and rotational loads. It is one of the most frequently injured structures during high impact or sporting activities. The ACL does not heal when torn, and surgical reconstruction is the standard treatment in the field of sports medicine. Such reconstruction aims at restoring the kinematics and stability of the injured knee, to prevent future degenerative changes.Therefore, an adequate understanding of the complex anatomy, function, and biomechanics of the ACL is critical to elucidate the mechanisms of injury, understand the fate of chronic ACL deficiency, and to improve surgical reconstruction.
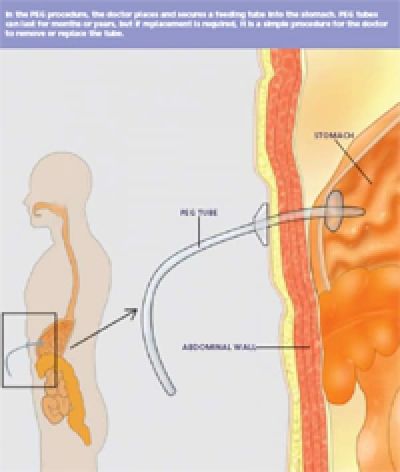
PEG stands for percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy, a procedure in which a flexible feeding tube is placed through the abdominal wall and into the stomach. PEG allows nutrition, fluids and/or medications to be put directly into the stomach, bypassing the mouth and esophagus. This brochure will give you a basic understanding of the procedure - how it's performed, how it can help, and what side effects you might experience.
In 1956, Erler and Itting designed a vacuum-compression unit that served as the prototype for the clinical model in use today. The device consists of a plexiglass chamber connected to a compressor. The unit provides a timed alteration of positive and negative pressures at a selectable range of intensities. Researchers believe that VCT systems do improve total tissue blood flow and oxygenation.
The phrase Rebound Therapy, when correctly applied describes a specific methodology, assessment, and programme of use of trampolines to provide opportunities for enhanced movement patterns, therapeutic positioning, exercise and recreation for a wide range of users with additional needs. It is used to enhance movement patterns, develop and promote motor skills, body awareness, balance, coordination, and communication. It is a highly enjoyable activity and is used to great effect as a cross-curricular teaching tool.
تماس سریع
شعبه مطهری: تهران، خیابان مطهری، بعد از قائم مقام فراهانی، خیابان فجر (جم)، کوچه مدائن، پلاک 20، ساختمان پزشکان ماهان، طبقه 3
02188492776شعبه شهرک غرب: تهران، شهرک غرب، فاز 1، خیابان ایران زمین، نبش خیابان گلستان جنوبی، پلاک 2
02188082255 02188078570شماره تماس 5 رقمی:
02141857محبوب ترین مطالب
مطالب پیشنهادی
طراحی شده توسط گروه طراحی و توسعه وب سایت رویال مدیا